Organ transplantation saves lives.According to the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network,U.S Department of Health and Human Services,over 22,000 organs transplantation surgeries have been conducted between January and September 2016.
Ischemia Reperfusion Injury (IRI) is a well characterized cardiac transplantation-related complication wherein the host tissue (graft),deprived of blood supply for prolonged periods,undergoes damage when blood supply is restored post-implantation.Immune cells at the interface of the graft and recipient tissue mediate damage by releasing inflammation-promoting chemicals and free radicals.
In a study led by Nadig and colleagues at the Department of Surgery,Division of Transplant,南卡罗来纳医科大学USA,researchers first acknowledge the central role played by endothelial cells (EC) in promoting IRI-associated tissue damage and subsequently developed a novel pH-sensitive,免疫抑制药物加载,靶向胶束纳米颗粒抑制ECS的破坏作用。The team choose rapamycin as their immunosuppressive drug of choice given its dual roles in limiting cytotoxic immune cell functions and in protecting tissues that make up blood vessels.
虽然在手术前用免疫抑制药物治疗患者是目前的标准做法,a major drawback of this approach is that these drugs prevent immune system activity throughout the body,placing patients at risk for diseases including diabetes and cancer.As an initial step in addressing this limitation,Nadig et al.coated the micelles with cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartate moieties,which specifically bind to and integrin protein (the alpha v beta 3 receptor protein) present almost exclusively on ECs.最后一点,研究小组将荧光化合物附在一起,以便在他们的研究中进行跟踪和可视化。
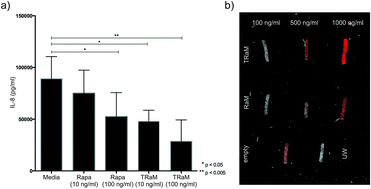
To demonstrate the clinical utility of their idea,the researchers exposed human endothelial cell cultures to hydrogen peroxide to mimic IRI-like conditions.这些细胞的反应是增加它们的炎症促进化学物质的产量。Importantly,the rapamycin-loaded nanoparticle micelles significantly curbed this response.Nadig et al.propose that the ultimate goal is to incorporate this technology into organ storage media to minimize the harmful effects of IRI.
Read the full article here:
RSC Adv.,2015,5,43552-43562
多伊:10.1039/C5RA04057D