 根据世界癌症报告的估计,到2030年,全球癌症相关死亡率预计将达到1700万。通过适当的临床干预来应对癌症负担,研究人员在单层细胞培养中筛选抗癌药物组合。这是一种广泛用于临床前药物疗效评价的方法。
根据世界癌症报告的估计,到2030年,全球癌症相关死亡率预计将达到1700万。通过适当的临床干预来应对癌症负担,研究人员在单层细胞培养中筛选抗癌药物组合。这是一种广泛用于临床前药物疗效评价的方法。
单层培养的一个主要限制是它们没有,even mildly,概述体内生长的肿瘤的复杂结构。As an initial step in overcoming this limitation,研究人员使用支架式球体培养物——一种细胞在水凝胶支架上三维生长的系统。
水凝胶支架为形成一个更“自然”的环境提供物理和结构支持,更好地在体内重现细胞行为。例如,smaller (150um) spheroids have better cell-to-cell contacts and notably different gene expression compared to monolayer cultures;larger (200-500um) ones develop oxygen and nutrient gradients reminiscent of chemical gradients seen in human tumors.然而,设计灵活性的局限性,handling and interbatch compositional variation have discouraged the routine use of hydrogel scaffolds.此外,在药物筛选之前,从支架材料中分离出新形成的球体是一个主要的技术难题。
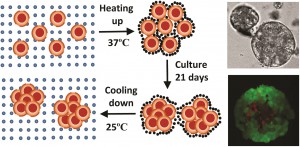
在崔晓林和他的同事领导的一项研究中,化学工程学院以及数学科学学院新利手机客户端,University of Adelaide,Australia,研究人员采用自由基乳液聚合法合成了一种热可逆N-异丙基丙烯酰胺-丙烯酸(NIPAM-AA)水凝胶。In their study using the cervical carcinoma cell line HeLa,研究小组证明,在370摄氏度时,NIPAM-AA水凝胶固化,并在HELA细胞簇周围形成鞘层。因此,随着时间的推移,这些团簇发展成水凝胶架式球体。在250℃时,水凝胶液化并释放出新形成的球体。
Cell viability assays confirmed that this new state of the art hydrogel is biocompatible.NIPAM-AA衍生的球体较小(70-120um)。近球形,与常规球体相比,尺寸分布更窄。研究表明,通过时间历程实验,球体在培养中的存活时间超过14天。The study also suggests that spheroids derived via the NIPAM-AA hydrogel method are more viable than those derived from conventional suspension cultures,支持水凝胶支架促进氧气和营养供应以支持细胞生长的观点。
研究人员推导了一个预测NIPAM-AA衍生球体生长动力学的数学模型。他们的模型准确地概括了增长率,球体的尺寸和尺寸分布。作者认为水凝胶支架有潜力发展成为一种应用广泛的技术,包括:但不限于:(一)用等径球体高通量筛选抗癌药物;(二)再生医学;(三)组织工程。
阅读全文: