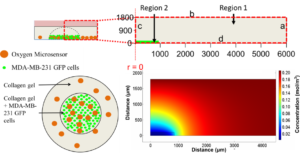
Microenvironmental oxygen levels and gradients within three-dimensional (3D) tissue cultures directly influence cellular behavior and function,决定扩散模式,metabolism and interaction of cells with each other and their environment.While advances and prevalence of体外generated 3D cultures have spurred new techniques and systems for biological interrogation,有必要开发和实施并行系统,以监测和表征组织培养物内及其周围用于培养的血管中的氧气微环境。Conventional oxygen evaluation platforms can be ill-suited for continuous oxygen evaluation in custom tissue cultures.The Takayama group was able to robustly evaluate multiple 3D culture platforms by combining the use of phase-fluorimetry and lab-fabricated dispersible oxygen responsive microparticles.氧微传感器用于评价两个球形培养血管。悬挂式液滴和低粘微孔板,强调两种培养技术中球体周围氧含量的变化。Dramatic differences can be seen in the steady state oxygen levels between the two culture techniques because of the difference in distance between the spheroids and the air-liquid interface in these two vessel types.These results highlighted the importance of minding the gas exchange location as compared to the cell culture to ensure appropriate tissue culture microenvironments.
Furthermore,these microsensors were used to map radial oxygen distribution across a circular,将微传感器分散在培养液中,形成细胞模式的水凝胶。Coupling the spatial oxygen mapping to computational models of oxygen diffusion,the authors were able to estimate oxygen uptake behavior of the tissue culture.而3D组织培养平台利用体外tissue architecture to produce more physiologically similar phenomena,integrated design and analysis of these 3D cell cultures from both biomaterial and oxygen supply aspects will be paramount in enabling researchers to effectively recreate some of the complexities present within both healthy and diseased tissues.
Tips from the authors:
- When fabricating oxygen microsensing beads,infusion with Dichloromethane enabled large amount of Ruthenium caging within the PDMS microspheres,while leaving them oxygen sensitive.而其他溶剂则更容易使PDMS膨胀,从而提高了对钌的注入效率。these solvents resulted in oxygen unresponsive ruthenium loaded PDMS beads.
- 微传感器不能有效地整合到我们用HEK293T试验过的多细胞球体中,hs-5和mda-mb-231细胞;as the spheroids contract microsensors are ejected out of the spheroids.
- The only limitation of phase-fluorimetry for the oxygen measurements is sufficient signal output that it can be detected by the photodiode,或其他检测系统。This was generally not a problem with beads greater than 80 microns assuming the culture systems was less than 1-mm thick.然而,我们无法有效地在80微米以下的珠子中注入足够的钌,使其具有来自微传感器的足够输出信号,从而获得大于1毫米的培养物的强大读数。
文章链接:
Dispersible oxygen microsensors map oxygen gradients in three-dimensional cell cultures 生物活性剂Sci.,2017,5,2106-2113
Dr.Sudip Mukherjee is a Web Writer forBiomaterials 新利手机客户端Science.He is currently a Postdoctoral Research Associate working alongside Dr.米斯大学生物工程系的奥米德韦瑟。His research is involved in the development of advanced nanomaterials for drug/gene delivery in cancer theranostics,immunomodulatory applications & angiogenesis.He published a total of ~30 research articles/patents.他是“材料研究快报”国际咨询委员会成员,IOP 新利手机客户端Sciences.He is an associate member (AMRSC) of RSC,UK.He serves as reviewer for several international journals like Chem Comm,J Mater Chem A,J Mater Chem B,生物医学纳米技术杂志,RSC Advances,IOP Nanotechnology etc.