Robert W. Style, John S. Wettlaufer和Eric R. Dufresne
This article proposes a theory of fluid inclusions in soft solids and builds upon experimental findings of a previous paper recently published in Nature Physics – “Stiffening solids with liquid inclusions” doi:10.1038/nphys3181 – which revealed that Eshelby’s foundational theory fails to describe the mechanical response of soft composites. Eshelby’s theory of elastic inclusions is significantly cited and outlines the response of microscopic inclusions within an elastic solid when macroscopically stress is applied. Furthermore, Eshelby’s theory allows the prediction of bulk properties and is fundamental in calculating the stress field in fracture mechanics. It has been widely used in many other areas such as cell biology to predict cell interactions and seismology.
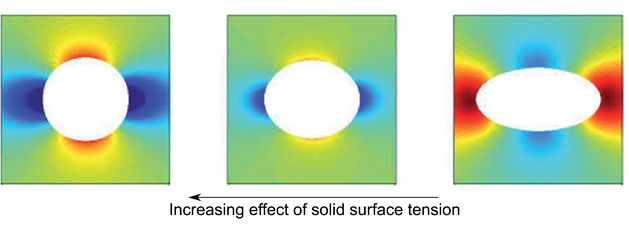
理论研究的目的是对前人的实验结果进行理顺,并解释这是由于固液界面的表面张力引起的,而这在现有的理论中是完全被忽略的。
这项工作扩展了先前基于应变相关表面应力的理论,该理论适用于硬度较高的材料中的纳米夹杂物,但不适用于凝胶等较软材料。
组适于使得它包括用于以线性的弹性固体液体包裹体的表面张力,得到的微观行为和夹杂物在复合材料中的宏观效应两者的Eshelby的夹杂理论。作者认为这些发现可应用到各种各样的软质材料的系统的,尤其是复合材料,其包括柔软的材料,例如凝胶和弹性体。
全部引文信息:
柔顺固体中液体夹杂物的表面张力和力学
拓拔风格,约翰S. Wettlaufer和Eric R.杜佛尼
软物质,2015年,第进展
DOI: 10.1039 / C4SM02413C