TheNanoscale Horizons编辑部很高兴宣布first文章发表过吗在线作为准备于2016年1月出版的第一期的先期文章。
Links to the first articles are below and are free to access until 2017.如果你想跟上尖端纳米科学研究的步伐,新利手机客户端sign up to the table of contents alerts在这里.
| Three dimensional nitrogen-doped graphene hydrogels with in situ deposited cobalt phosphate nanoclusters for efficient oxygen evolution in a neutral electrolyte Anthony Vasileff,Sheng Chen and Shi Zhang Qiao |
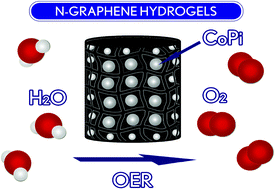 A hybrid electrode of cobalt phosphate (CoPi) on nitrogen doped graphene hydrogels was fabricated by hydrothermal treatment of graphene oxide followed by CoPi electrodeposited in situ,在中性电解质中表现出良好的氧反应性能。 Nanoscale Horiz.,2016年,doi:10.1039/c5nh000002e
|
| Pressing a spring: what does it take to maximize the energy storage in nanoporous supercapacitors? Svyatoslav Kondrat和Alexei A.科尔尼雪夫 |
 We discuss the nonlinear effects and efficiency of charge storage in supercapacitors with nanoporous electrodes and ionic liquids,并证明为了最大限度地利用储能,这可能有利于在充电过程中产生“障碍”或“困难”。This can be achieved by making thermodynamically unfavourable conditions for ions inside nanopores,or more favourable outside.我们通过蒙特卡罗模拟表明,这种“离子恐惧”孔能更有效地储存能量,并能提供同等甚至更好的能量容量。由于最近的分析预测了憎离性纳米孔充电更快,我们得出的结论是,这种孔隙为同时优化能量/功率提供了更好的选择。 We discuss the nonlinear effects and efficiency of charge storage in supercapacitors with nanoporous electrodes and ionic liquids,并证明为了最大限度地利用储能,这可能有利于在充电过程中产生“障碍”或“困难”。This can be achieved by making thermodynamically unfavourable conditions for ions inside nanopores,or more favourable outside.我们通过蒙特卡罗模拟表明,这种“离子恐惧”孔能更有效地储存能量,并能提供同等甚至更好的能量容量。由于最近的分析预测了憎离性纳米孔充电更快,我们得出的结论是,这种孔隙为同时优化能量/功率提供了更好的选择。 Nanoscale Horiz.,2016,内政部:10.1039/c5nh00004a |
| 白色念珠菌与巨噬细胞的纳米级粘附力 索菲亚·艾尔·基拉特·查特尔和伊夫·F.Dufrene |
 真菌感染的发展受到真菌病原体与宿主免疫细胞相互作用的严格控制。While the recognition of specific fungal cell wall components by immune receptors has been widely investigated,the molecular forces involved are not known.在这次交流中,we show the ability of single-cell force spectroscopy to quantify the specific adhesion forces between the fungal pathogen Candida albicans and macrophages.The Candida–macrophage adhesion force is strong,up to ∼3000 pN,与巨噬细胞膜上表达的凝集素受体和真菌细胞表面甘露聚糖碳水化合物之间的多重累积键相对应。粘附力信号显示恒定的力高原,up to >100 μm long,反映了从巨噬细胞膜上提取延长的系链,a phenomenon which may increase the duration of intercellular adhesion.粘合力随时间增强,提示巨噬细胞膜在初次接触后迅速吞噬病原体,leading to its internalization.The force nanoscopy method developed here holds great promise for understanding and controlling the early stages of microbe–immune interactions. Nanoscale Horiz.,2016,DOI: 10.1039/C5NH00049A |
| 磁可调胶体微镜 James GoeblYiding Liu,Sandy Wong,Serkan Zorba and Yadong Yin |
 Herein we demonstrate a method for decorating highly reflective 2D gold microplates with magnetic nanoparticles to produce an optical colloid that can be actuated using an applied magnetic field.These magnetic micromirrors can be rapidly rotated and exhibit a strong contrast in reflectance between the "on" and "off" states. Nanoscale Horiz.,2016,DOI: 10.1039/C5NH00035A |
| 柔性超级电容器用二氧化锰纳米材料:通过本征和非本征修饰提高性能 腾翟,Xihong Lu,Fuxin Wang,Hui Xia and Yexiang Tong |
 Increasing power and energy demands for next-generation portable and flexible electronics have raised critical requirements (flexibility,stretch-ability,environmental friendliness,lightweight, etc.) for the energy storage devices.Flexible supercapacitors (SCs),作为最有前途的下一代储能装置之一,由于其体积小等突出特点,引起了人们的浓厚兴趣。low weight,操作方便,excellent reliability,and high power density.Manganese oxide (MnO2),has attracted much interest in the development of flexible SCs with high electrochemical performance.Yet,二氧化锰电极的电子和离子输运性能差,限制了其在实际应用中的推广。本文综述了近年来二氧化锰材料在柔性SCS开发中的应用进展,总结了通过结晶作用对二氧化锰进行的内在改性。crystal structure,以及通过非三维(3D)和三维柔性导电支架引入氧气空位和对二氧化锰进行非本征改性,以实现高性能柔性SCS。此外,we also discuss briefly on the current challenges,未来方向,and opportunities for the development of high-performance MnO2 based flexible SCs. Increasing power and energy demands for next-generation portable and flexible electronics have raised critical requirements (flexibility,stretch-ability,environmental friendliness,lightweight, etc.) for the energy storage devices.Flexible supercapacitors (SCs),作为最有前途的下一代储能装置之一,由于其体积小等突出特点,引起了人们的浓厚兴趣。low weight,操作方便,excellent reliability,and high power density.Manganese oxide (MnO2),has attracted much interest in the development of flexible SCs with high electrochemical performance.Yet,二氧化锰电极的电子和离子输运性能差,限制了其在实际应用中的推广。本文综述了近年来二氧化锰材料在柔性SCS开发中的应用进展,总结了通过结晶作用对二氧化锰进行的内在改性。crystal structure,以及通过非三维(3D)和三维柔性导电支架引入氧气空位和对二氧化锰进行非本征改性,以实现高性能柔性SCS。此外,we also discuss briefly on the current challenges,未来方向,and opportunities for the development of high-performance MnO2 based flexible SCs. Nanoscale Horiz.,2016,DOI:10.1039/c5nh00048c |
| Size-tunable rhodium nanostructures for wavelength-tunable ultraviolet plasmonics Xiao Zhang,Pan Li恩格拉·巴雷达,Yael Guti_rrez,弗朗西斯科·冈兹·莱兹,Fernando Moreno,Henry O.埃弗里特和刘杰 |
 Polydisperse rhodium nanoparticles have recently shown promise for ultraviolet (UV) plasmonics,but controlling the size and morphology of metal nanoparticles is essential for tuning surface plasmon resonances.Here we report the use of slow-injection polyol methods to synthesize monodisperse Rh nanocubes with unprecedentedly large sizes and slightly concave faces.The associated local surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) red-shifted with increasing sizes in the UV region from deep UV to around 400 nm,与数值模拟一致。附着在Rh纳米管上的对氨基硫酚的紫外照射产生表面增强拉曼光谱和加速光分解,这些增强对于LSPR与紫外激光共振的纳米管来说是最大的。缺乏天然氧化物涂层,精确控制纳米管的尺寸和形态。and the ability to tune the surface plasmon resonance from the deep UV to near UV spectral region,使铑成为紫外等离子体应用的一个引人注目的选择。 Nanoscale Horiz.,2016,DOI: 10.1039/C5NH00062A |
| Ultrasensitive optical detection of anions by quantum dots Yongbing Lou,赵一新、朱俊杰 |
 量子点(qds)由于其独特的光物理性质,如可调谐带隙等,在过去几十年中受到了广泛应用的关注。易于溶液加工和不同配体的多功能表面功能化。开发了高灵敏度、高选择性的量子点光学分析技术,用于环境监测水溶液中阴离子的检测。医疗诊断,以及生物样品和工业过程的分析。Here we review the latest research progress of semiconductor QDs for sensing of anions in aqueous solution orin vivo,and discuss the photophysical mechanisms and outlook for the potential development in QD based optical sensing for anions. Nanoscale Horiz.,2016,doi:10.1039/c5nh00039d |